Note
Click here to download the full example code
Miscellaneous ways to use polar projections¶
Polar projections allow plotting polar coordinate data (e.g. angle \(\theta\) and radius r).
The full syntax for polar projections is:
Pwidth[+a][+f[e|p|radius]][+roffset][+torigin][+z[p|radius]]
Limits are set via the region parameter
([theta_min, theta_max, radius_min, radius_max]). When using
Pwidth you have to give the width of the figure. The lower-case
version p is similar to P but expects a scale instead of
a width (pscale).
The following customizing modifiers are available:
+a: by default, \(\theta\) refers to the angle that is equivalent to a counterclockwise rotation with respect to the east direction (standard definition); +a indicates that the input data is rotated clockwise relative to the north direction (geographical azimuth angle).
+roffset: represents the offset of the r axis. This modifier allows you to put the center of the circle not to r=0.
+torigin: sets the angle corresponding to the east direction which is equivalent to rotating the entire coordinate axis clockwise; if the +a modifier is used, setting the angle corresponding to the north direction is equivalent to rotating the entire coordinate axis counterclockwise.
+f: reverses the radial direction.
Append e to indicate that the r-axis is an elevation angle, and the range of the r-axis should be between 0 and 90.
Appending p sets the current earth radius (determined by PROJ_ELLIPSOID) to the maximum value of the r axis when the r axis is reversed.
Append radius to set the maximum value of the r axis.
+z: indicates that the r axis is marked as depth instead of radius (e.g. r = radius - z).
Append p to set radius to the current earth radius.
Append radius to set the value of the radius.
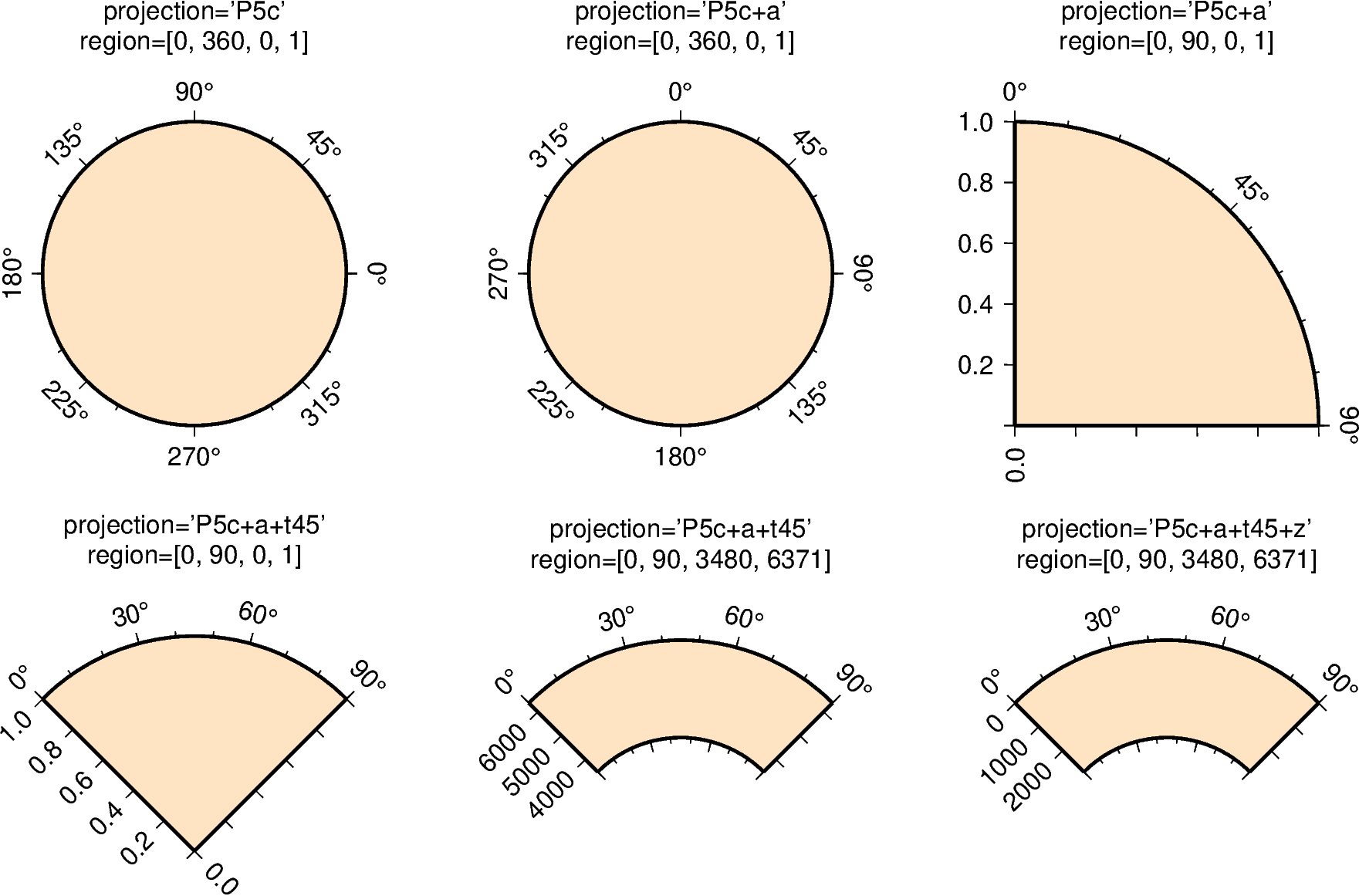
Out:
<IPython.core.display.Image object>
import pygmt
fig = pygmt.Figure()
pygmt.config(FONT_TITLE="14p,Helvetica,black", FORMAT_GEO_MAP="+D")
# ============
fig.basemap(
# set map limits to theta_min = 0, theta_max = 360, radius_min = 0, radius_max = 1
region=[0, 360, 0, 1],
# set map width to 5 cm
projection="P5c",
# set the frame and color
frame=["xa45f", "+gbisque"],
)
fig.text(position="TC", text="projection='P5c'", offset="0/2.0c", no_clip=True)
fig.text(position="TC", text="region=[0, 360, 0, 1]", offset="0/1.5c", no_clip=True)
fig.shift_origin(xshift="8c")
# ============
fig.basemap(
# set map limits to theta_min = 0, theta_max = 360, radius_min = 0, radius_max = 1
region=[0, 360, 0, 1],
# set map width to 5 cm and interpret input data as geographic azimuth instead
# of standard angle
projection="P5c+a",
# set the frame and color
frame=["xa45f", "+gbisque"],
)
fig.text(position="TC", text="projection='P5c+a'", offset="0/2.0c", no_clip=True)
fig.text(position="TC", text="region=[0, 360, 0, 1]", offset="0/1.5c", no_clip=True)
fig.shift_origin(xshift="8c")
# ============
fig.basemap(
# set map limits to theta_min = 0, theta_max = 90, radius_min = 0, radius_max = 1
region=[0, 90, 0, 1],
# set map width to 5 cm and interpret input data as geographic azimuth instead
# of standard angle
projection="P5c+a",
# set the frame and color
frame=["xa45f", "ya0.2", "WNe+gbisque"],
)
fig.text(position="TC", text="projection='P5c+a'", offset="0/2.0c", no_clip=True)
fig.text(position="TC", text="region=[0, 90, 0, 1]", offset="0/1.5c", no_clip=True)
fig.shift_origin(xshift="-16c", yshift="-7c")
# ============
fig.basemap(
# set map limits to theta_min = 0, theta_max = 90, radius_min = 0, radius_max = 1
region=[0, 90, 0, 1],
# set map width to 5 cm and interpret input data as geographic azimuth instead
# of standard angle, rotate coordinate system counterclockwise by 45 degrees
projection="P5c+a+t45",
# set the frame and color
frame=["xa30f", "ya0.2", "WNe+gbisque"],
)
fig.text(position="TC", text="projection='P5c+a\+t45'", offset="0/2.0c", no_clip=True)
fig.text(position="TC", text="region=[0, 90, 0, 1]", offset="0/1.5c", no_clip=True)
fig.shift_origin(xshift="8c", yshift="1.3c")
# ============
fig.basemap(
# set map limits to theta_min = 0, theta_max = 90, radius_min = 3480,
# radius_max = 6371 (Earth's radius)
region=[0, 90, 3480, 6371],
# set map width to 5 cm and interpret input data as geographic azimuth instead
# of standard angle, rotate coordinate system counterclockwise by 45 degrees
projection="P5c+a+t45",
# set the frame and color
frame=["xa30f", "ya", "WNse+gbisque"],
)
fig.text(position="TC", text="projection='P5c+a\+t45'", offset="0/2.0c", no_clip=True)
fig.text(
position="TC", text="region=[0, 90, 3480, 6371]", offset="0/1.5c", no_clip=True
)
fig.shift_origin(xshift="8c")
# ============
fig.basemap(
# set map limits to theta_min = 0, theta_max = 90, radius_min = 3480,
# radius_max = 6371 (Earth's radius)
region=[0, 90, 3480, 6371],
# set map width to 5 cm and interpret input data as geographic azimuth instead
# of standard angle, rotate coordinate system counterclockwise by 45 degrees,
# r axis is marked as depth
projection="P5c+a+t45+z",
# set the frame and color
frame=["xa30f", "ya", "WNse+gbisque"],
)
fig.text(position="TC", text="projection='P5c+a\+t45+z'", offset="0/2.0c", no_clip=True)
fig.text(
position="TC", text="region=[0, 90, 3480, 6371]", offset="0/1.5c", no_clip=True
)
fig.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 4.475 seconds)